Mukesh Jain

Most of the 19th and 20th Century Psychology was consumed by a single topic – mental illness. Freud, one of the greatest names in traditional clinical psychology advocated the psychiatric and psychoanalytic therapy practices wherein patients are encouraged to dig into their past for the negative events and impulses that have led to the formation of their identities.
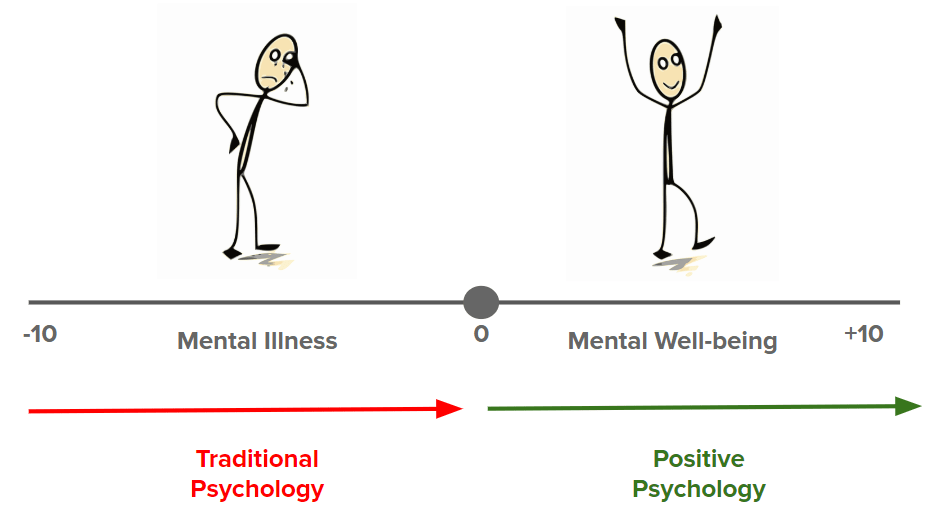
Martin Seligman, a famous psychologist who in 1998 was appointed as the President of the American Psychological Association, proposed a new movement in the field of psychology, which will focus on the positive aspects of human life such as happiness, well-being, and flourishing. His logic was quite simple: people want more than just to correct their weaknesses. People do not just want to vegetate but want lives infused with meaning. Thus, the need was felt to change the focus from shortcomings of human being to human potential. The approach of positive psychology was thus not targeted at fixing the problems, but on finding out that make life worth living. It was, as was quoted often, concerned not with how to transform, for example, -10 to -3, but with how to bring + 3 to + 10. With this background, Martin Seligman and Csikszentmihalyi, gave a formal definition to positive psychology: “the scientific study of optimal human functioning that aims to discover and promote the factors that allow individuals and communities to flourish and thrive”.
In short, positive psychology is the scientific study of optimal human functioning that aims to discover and promote the factors that allow individuals and communities to thrive. Or, as Dr. Christopher Peterson put it: positive psychology is the study or what makes life most worth living. It’s the study of what’s right with you, not what’s wrong.

Below, you’ll see Dr. John Travis’s illness-wellness continuum, showing that there are several degrees of both illness and wellness. Positive psychology focuses on moving people first to the neutral point and then as far toward wellness as possible. As many sober and sober curious folks have experienced, sometimes getting to the neutral point is the best we can do and sometimes moving to awareness, education, and growth take time. We’re here to take that time, together. We’re here to learn, together. We’re here to grow, together.
Positive psychology is the study of optimal functioning. It examines the psychological resources and characteristics that allow people to function adaptively in the face of the many demands of life. An orienting principle of this approach is that removing the factors that lead to pathology, deficits, or failure is not sufficient to build mental health or promote flourishing. Instead, this requires an understanding of the factors that make life worth living such as happiness, success, and virtue. Positive psychology adopts a strengths perspective, examining what each individual does well. This approach, however, does not replace pre-existing paradigms; instead it offers a complement to help promote understanding of the determinants and consequences of living well.
The central tenets of positive psychology include the following: (1) positive and negative aspects of functioning do not lie on a bipolar continuum but instead represent unique dimensions (i.e., happiness is not the opposite of unhappiness), (2) hypothetically moving from a + 2 to a + 5 requires different techniques than moving someone from a – 5 to a – 2, (3) working on strengths is more beneficial than working on weaknesses, and (4) psychology needs to understand what allows people to flourish just as it aims to understand the characteristics and factors that predispose individuals to languish. Martin Seligman, the father of positive psychology, after a lot of solid evidence-based research on the subject proposed the PERMA model of wellbeing. PERMA is an acronym for the five elements of wellbeing according to Seligman.
– P – Positive Emotions (Feeling Good)
– E- Engagement (Being completely absorbed in activities)
– R- Relationship (Being authentically connected to others).
– M – Meaning (having a purposeful existence)
– A – Achievement (sense of success and accomplishment)
Dr Mukesh Jain is a Gold Medallist engineer in Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering from MANIT Bhopal. He obtained his MBA from the Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad. He obtained his Master of Public Administration from the Kennedy School of Government, Harvard University along with Edward Mason Fellowship. He had the unique distinction of receiving three distinguished awards at Harvard University: The Mason Fellow award and The Lucius N. Littauer Fellow award for exemplary academic achievement, public service & potential for future leadership. He was also awarded The Raymond & Josephine Vernon award for academic distinction & significant contribution to Mason Fellowship Program. Mukesh Jain received his PhD in Strategic Management from IIT Delhi.
Mukesh Jain joined the Indian Police Service in 1989, Madhya Pradesh cadre. As an IPS officer, he held many challenging assignments including the Superintendent of Police, Raisen and Mandsaur Districts, and Inspector General of Police, Criminal Investigation Department and Additional DGP Cybercrime, Transport Commissioner Madhya Pradesh and Special DG Police.
Dr. Mukesh Jain has authored many books on Public Policy and Positive Psychology. His book, ‘Excellence in Government, is a recommended reading for many public policy courses. His book- “A Happier You: Strategies to achieve peak joy in work and life using science of Happiness”, received book of the year award in 2022. After this, two more books, first, A ‘Masterclass in the Science of Happiness’ and the other, ‘Seeds of Happiness’, have also been received very well. He is a visiting faculty to many business schools and reputed training institutes. He is an expert trainer of “Lateral Thinking”, and “The Science of happiness” and has conducted more than 300 workshops on these subjects.

